‘Obsessive?’ ‘Obsessive!’ Yes, indeedy.
From little asides big myths grow. The sum total of human knowledge of Atlantis comes from a couple of pages in two of Plato’s dialogues, the ‘Timaeus’ and the Critias.’ These two are not in the first rank of Platonic dialogues. A great many admirers and readers of Plato have never heard of them.
The ‘Timaeus’ is a conversation set the day after the conclusion of the discussion of the ‘Republic.’ (Since there is no republic in it, for millenia pedants always wonder about that title. Answer: It was bestowed on the work by Cicero hundreds of years after Plato’s death. Cicero was not much interested in accuracy, think of him as a Fox journalist. No doubt it suited his purpose to have Plato legitimate a republic on the assumption that no one else would read the whole book.)
In turn, the ‘Critias’ continues the ‘Timaeus.’ In the few lines that mention Atlantis it is at a great remove from Plato. It is allegedly a story that an Egyptian told Solon hundreds of years earlier that is reported by one of the interlocutors. It mixes very specific details like the colour of building blocks, and the measurements of temple while being maddeningly vague about where the place was except for a reference that has been translated as ‘beyond the pillars of Hercules.’
What with all his labours, Hercules seems to gotten around the Mediterranean. Atlantologists have located the pillars at Gibraltar, Malta, Messina, Crete, Santorini, Morocco, the Crimea, and, believe it or not, Ireland. Yes, Ripley this really is ‘Believe it or not’ country.

Our cicerone is not quite right in that subtitle above. The book is not about his quest so much as that the other Atlantogolists he seeks and meets. Some he sought out in libraries and archives, and others on the internet, and he went to meet many of them in person. The book is a travelogue about the Atlantologists from Ireland, Germany, Morocco, Sicily, Greece, Malta, United States, Great Britain, and more. He had some travel budget did Mark.
The one place bruited as Atlantis that he did not visit was…. Antartica. Yes, Antartica has been identified by some as Atlantis, which drifted south after a cataclysm.
The tone is light and the prose snappy. While he is not a true believer in the Big ‘A,’ there are no cheap shots at those who do believe in Atlantis. This is no Bill Bryson hatchet job passed off as humour.
He does call the many interpretations of Atlantis ‘theories’ and that annoyed me because they are speculations, not theories. A theory joins evidence and analysis. Speculation is guess work without either.
The many ways in which Plato’s few lines are interpreted include, deciding that he meant 900 and not 9000, and the latter is a transcription error made by a scribe in ancient Egypt. Well, yes, it could be, and that scribe might have had red hair but however are we to know?
As for the ‘pillars of Hercules,’ every part of that is deconstructed and reconstructed to suit the desires of the speaker. ‘Pillars’ can refer to many things, far more than I ever thought. And Hercules, well he was several other chaps with the same name all over the place like John Smith. On it goes. The Wikipedia entry is a site of constant conflict. It changes every day as the Atlantologists slug it out on their keyboards.
When I first read the ‘Timaeus’ I thought the reference to Atlantis there was an undeveloped allegory on the hubris of peoples, not a road map. I took it to be a parallel of the Allegory of the Cave, and no one has yet set out to find that very CAVE. Silly me, once again I missed the point.
Some of the Atlantologists he met are safe, safe, and sober who discount the wild speculations of the many more zealous of their number, but find the subject fascinating. One of these triple esses (safe, sane, and sober) runs a web site: atlantipedia.ie.
Others are obsessive, no doubt about it. Any claim Mark Adams has to be being obsessive is bleached out by some of the characters he met. Among them are those that cannot make eye contact, talk in 45 minutes monologues and then lapse into catatonic states, talk to him through doors for security reasons (someone might steal my Atlantis map if I let anyone in). These are not in the safe, sane, an sober zone of inquiry.
Some promote a location, like Sicily, Santorini, or Malta, as Atlantis for purely venal reasons: it brings a few tourists (even if they are nut-cases, they pay hotel bills).
 One of many maps on the internet.
One of many maps on the internet.
Mixed in among these types are a collection of serious archeologists who are studying ancient ruins here and there and whose work, an Atlantologist thinks, has something to do with Atlantis. Huh? Well, goes the interpretation, these archeologists keep secret their interest in Atlantis, (a) because of the conspiracy of the rose (on this, see below) or (b) their funding would be cut if they admitted it. Maybe this is the paranoid side of the coin. Or (c) they foolishly do not realise the connection to Atlantis.
 One of many representations of a building on Atlantis.
One of many representations of a building on Atlantis.
Francis Bacon (1561–1626) called his little book in praise of science ‘The New Atlantis’ and in it speculated on what science could do to conquer nature and improve humankind. Because of the great powers of science for ill as well as good, Bacon imagined its use confined to a sect who worked with this secret knowledge for the good of all on an island. (Yes, this is the same Bacon who wrote the complete work of Shakespeare according to some….)
 Francis Bacon (I have seen this image passed off as Machiavelli more than once, believe it or not, Ripley.)
Francis Bacon (I have seen this image passed off as Machiavelli more than once, believe it or not, Ripley.)
Fatherhood followed. He sired, as so many have claimed, without knowing it, Rosicrucianism. This doctrine has followers today at your nearest public library, though they will not wear a rose on the lapel.
 The rose cross,
The rose cross,
Start checking out, reading, asking about books on Francis Bacon and the Followers of the Rose will ever so subtly make themselves known. They live and breathe conspiracy, arcane knowledge, numerology, and a lot else not to be found on the curriculum at a university. (Not yet, anyway. I omit Pepperdine, where shoe tying is an advanced course.)
 Where else? California near San José.
Where else? California near San José.
It is proof positive that Atlantis existed to the Rosicrucians that NASA named a space shuttle Atlantis. That was, they say, a coded message not only to Earthlings, but to aliens, as well. Gulp! Yes, there is an Erich van Donkey element to all this. The spell-checker changed the egregious Swiss hotelier’s name to Donkey and I decided to accept it as fitting.
Adams meets a few of the adherents of the rose along the way, nods a lot in agreement with them, hides in the bathroom to avoid others, and leaves town as soon as possible when he encounters a coven of them. Reading of his experiences made me wonder the Rosicrucians had never figured in ‘Midsomer Murders.’
Jules Verne, Walt Disney, Star Gate, an eponymous television series in 2013, and scores of others have made use of the name recognition of Atlantis, and in so doing have scattered its seed further, and by repetition perhaps planted it deeper. A google search returns a gazillion hits or 110,000,000 without even working up a sweat.
 Mark Adams
Mark Adams
Having made light of it all above, I must conclude by saying that Adams does shift the evidence and evaluate the arguments he heard, without denigrating anyone, and concludes, with a phalanx of qualifications, that the ancient city of Tartessos near Cadiz in Spain is the best candidate. That is, if there ever was an Atlantis. This city has a genealogy as Tartessos but perhaps Atlantis previously occupied the site before it was obliterated in a tsunami. As to the details Plato gives of colours and dimensions, these might simply be artistic touches of verisimilitude that can be dismissed. Hey, presto! We have arrived at Atlantis!
Thus inspired I re-read the ‘Timaeus’ and the ‘Critias’ to see for myself where the fire started. The reference to Atlantis is brief in the former and continued in some tantalising detail in the latter. In the ‘Timaeus.’ An Egyptian priest told Solon, who upon his return to Greece told Dropicles, who told Critias’s grandfather who told his grandson also named Critias. These four tellings span the two hundred years from Solon to Plato. That make me think of those ‘pass it on’ exercises in school. The teacher whispers in the ear of the first child ‘The sky is blue,’ now tell your neighbour and by the time it went around the class, the ceiling was falling. The morale of the story in that case was do not believe everything said.
The ‘Critias’ has all those details that have set Atlantological hearts a-pounding. Distance, dimensions, durations, depths, and more, all of which are well canvassed by Adams.
Reading it now the point of the story seems to me to this: As big and powerful and grand as Atlantis was, our noble ancestors, the Athenians, defeated them. Atlantis had all the wealth and power but this pre-historic Athens had all the virtue: they held all things in common, the warriors lived apart as warriors, features in the fictional city of the ‘Republic’ now given an Athenian pedigree and a track record of success. And why does not the Greek in the street know this already, why because a flood swept away Atlantis and most of Greece, too, so angry was Poseidon at the hubris of the Atlanteans. This devastating flood killed all the literate men who might have remembered or recorded the story, sparing only a few rude and crude mountain men from whose loins Athens was eventually re-populated. This flood stripped Attica of its topsoil and carved the Athenian acropolis out. End of story.
Get it? Atlantis was big and powerful but no match for a virtuous Athens. Athens was virtuous because no one there cared about gold, jewels, luxuries that the Atlanteans had in plenty.
Author: Michael W Jackson
René Lévesque (2013) by Daniel Poliquin
René failed because he succeeded. Ever a paradox.
Many people loved René and many people hated him, and still more both loved and hated him. He is the one person whom I would say was charismatic. He burned with a message akin to those religious prophets that Max Weber coined the word to describe. I saw him once in person in a very small audience in Edmonton, and many times later on television. There are plenty of clips on You Tube. But, well, you had to be there to feel the electricity in the air. At the 1980 defeat the rapturous crowd response and his simple and direct statement: ‘I understand’ perhaps suggest his quality. Remember this is the leader addressing the troops in defeat. It is on You Tube.
The book does not try to be a biography inquiring into the growth and shaping of the man, but is rather a summary of his life and career. It filled in many gaps for this casual observer.

Readers who do not know René can start with the three facts.
1. He was always called René by everyone from bus drivers. journalists, enemies, admirers, voters, opponents, to body guards. Like the eponymous television characters Lovejoy or Morse, René had only one name.
2. When he resigned from office after nearly a decade and cleared out his one bedroom apartment where a plastic milk crate served as a coffee table, he took away his worldly belongings in a plastic supermarket bag. He had long ago given his apartment in Montréal to his divorced wife. (He lived his short years in retirement on his parliamentary pension.)
3. The epitaph from one close and sympathetic English-Canadian observer was: his words stopped more than one riot.
He was from Gaspé, a distant and isolated region where the living is hard, but his family had connections. He was a lousy student and dropped out of Laval University in 1944 for military service. But unlike the Québécois hero of Hugh MacLennan’s ‘The Two Solitudes’ he did join the Canadian army.
René did everything his way: He went south and enlisted as a translator and liaison officer in the United States army serving in Europe with Patton’s Third Army. He saw Dachau within days of it liberation, and that vision stayed with him for the rest of his days. In 1950 he went to Korea as a correspondent, this time with Canadian troops.
Like many, veterans and not, he later embellished these experiences in many ways, but somehow managed to live those fictions down. He did tell lies, to make it plain.
The author suggests three legacies his 1944 experiences that forever shaped the man:
1. Democracy. He arrived in London in 1944 to a society under siege, yet he saw Hyde Park orators excoriating Britain for its coloniziation of India. Here was a country on its knees, everything rationed so thin as not to exist, with nearly every man and woman in a crude uniform – some with wooden rifles, V-rockets falling every day killing thousands, and yet during all-clears polite Indian orators excoriated England to attentive and polite crowds. If that was democracy, it was what he wanted.
2.Les maudits Français. He never had any interest in or respect for France. Later when he met French presidents and foreign ministers, he seldom did more than go through the motions. De Gaulle’s (in)famous remark from the balcony of town hall in Montréal, sent René into a rage. Another Frenchman interfering in something he does not understand. More colonialism!
3. Dachau was the outcome of blind nationalism. Never will he do, say, or acknowledge anything that goes down that road.
He become first a radio broadcaster and then a television presenter who explained the world to Québécois(e) in the 1950s. The backward nature of Québec in the period is hard to believe. Maybe one fact says it all. In 1875, yes in 1875, the provincial government of Québec abolished its Department of Education. It vacated education, leaving it to the Catholic Church. Few children went beyond 6th grade. Most girls left sooner. The curriculum was approved in Rome.
On television his genius for keeping it simple paid off. He soon had his own program ‘Point de mire’ (Focus). The author makes it clear what a refreshing breadth of air he was on a medium largely dominated by the sanctimonious and inscrutable at the time. His viewers were working class Québécois(e) and he spoke directly to them. Other presenters spoke Parisienne French, many were from The Church, some even spoke Latin on Radio Canada, most talked either down to the audience or over its head. All were dead boring. (For the literal minded, note that Radio Canada broadcasts both radio and television.)
Then came La Revolution Tranquil and he was recruited as a Liberal candidate and within weeks was a cabinet minister. He had zero (0) relevant experience. He had never managed a staff or a budget, and had never delivered anything concrete. Yet he was a whirlwind.
In a few weeks he convinced a cabinet, where there were many long-serving foot soldiers who resented this celebrity candidate, to nationalize electricity!
 René, ‘My way or else!’
René, ‘My way or else!’
Hydro-Quebec was born, and it employed French-speaking engineers, accountants, technicians, specialists, receptionists, linesmen, repair crews, damn builders, managers, and secretaries. These skills in turn had to be learned and taught, and the Department of Education was rejuvenated.
 The Québec flag atop a building with the Hydro-Québec logo
The Québec flag atop a building with the Hydro-Québec logo
Along the way he upset many apple carts, like putting every contract to public tender. Incoming Liberals had rather been counting on rewarding supporters with contracts on the sly, and here was a minister who made it all public. Reluctantly, others had to follow…the leader. He also closed his door to contractors who wanted to woo him. Non! It all goes through channels and all the channels are public. Again other ministers found they had to do likewise.
The old saying is that every Québécois is an independentist at least an hour a day. René’s experiences as a minister led him quickly to conclude that Québec could only become a modern society if it ran its own house. The financiers in Toronto called the shots to benefit themselves. The Church wanted acquiescent worshippers. The politicians in Ottawa were always looking to an abstraction called Canada. For both, leaving Québécois to hew trees for paper and draw water for hydo-electricity was enough. Backward, barefoot, and pregnant would be fine. The colourful natives can stay that way.
In a few years he started a movement to secure a special relationship for Québec within Canada that morphed into the Parti Québécois, and a few years later he was the PQ premier of Quebec. It was a roller coaster ride.
He prevented riots. When Pierre Trudeau faced down the rioters himself in 1968, René was also hosing down the hot heads, and he had a lot more credibility with them than Trudeau. These two, Trudeau and René, were well acquainted and they lined up on different sides, Trudeau for Canada first and last, and René for Québec first and last. For a decade or more their axis dominated Canadian politics. Each had wins; each had loses.
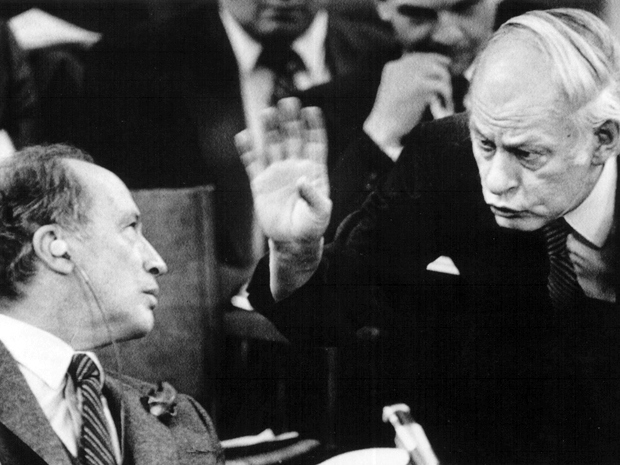 Pierre Trudeau and René Lévesque
Pierre Trudeau and René Lévesque
The rough rides included the FLQ crisis and the War Measures Act that put armed troops on the streets of Montréal. As much as René reviled the War Measures, he was the first and the loudest to condemn the FLQ and stopped more riots. Years later when a convicted FLQ member (having served his time and out of jail) entered a PQ rally, René slammed down the microphone and stormed out. He would NOT be in the same room with that murdering scum. (Though that individual was not himself a murder, he had conspired with them.)
This latter was a card he played often to keep in line the Saint Bartholomew’s circus that comprised the PQ. Do it my way or get a new leader!
A few more bumps in the rough ride include these: two failed referenda on sovereignty, manslaughter, a soldier shooting up the Assemblé Nationale in Québec Cité, and a double agent. Who said Canadian politics is dull?
René the democrat accepted the referenda results, and saw to it that even the zealots in the PQ accepted the results, too. That took a lot of doing, and another threat to quit. Another riot averted.
A Canadian soldier killed three people in the Assemblé Nationale in an effort, he said, to destroy the PQ government. René was not in the building at the time but he hosed down the reaction. No riot this time either.
The manslaughter occurred when René drove home after a long, acrimonious meeting in a bitter January winter snowfall, having drunk — no doubt too much — French wine he ran over and killed a homeless man. The victim was well known to the police for harassing motorists and lying on the road to make them stop so he could ask the drivers for money. René ran over and killed him in the snowfall and called the Sûreté du Québec. Given his many enemies, including aspiring rivals in the PQ, that he was exonerated is convincing. (Note: my driving experience in Montréal left me with a strong impression of hostile and aggressive pedestrians. Nowhere else did I met people who, passing by, yanked open the car door to ask for money, a ride, or pass an opinion on out-of-province license plates.) This event is recounted in Michel Basilieres’s Québec Northern Gothic novel ‘Black Bird’ (2004), which I enjoyed enormously.
The double agent? It turned out that one of René’s closest cabinet colleagues had been recruited years earlier by the Gendarmerie Royal du Canada (RCMP) to inform on radical student groups and he continued to take the payment thereafter. When confronted with the facts, as only René could do, face-à-face, the minister argued he had penetrated the RCMP for the cause! An explanation that René did not dignify with a reply. Well, he did reply: NON!
Perhaps René’s finest hour came the day after he resigned as premier. There was the ceremonial dinner. It was all conducted in French among 600 guests from the political, administrative, media, lobbying classes. At the end René spoke English to invite the one person, having sat through several hours, who spoke no French to join him on the podium and to speak to the assembled group in his language. This man who had come a long way at his own expense spoke Inuit and thanked René for his years of effort at improving the lives of the First People above the Arctic Circle. Indeed, René had done so much that other provincial premiers and finally the Federal Government had had to match his efforts in education, health, welfare, and more.
But the medium was also the message. We can speak our language; so can he.
That should whet any appetite. There is more in the book.
The author pulls no punches and it is a better book for it. René told lies at times. He was prone to self-dramatisation, as if his life did not have enough drama. He was bad father and a terrible husband, and treated the many women in his life as disposable. The confrontational ‘F off, I am indispensable, and you’re not’ was used too often later in life when the patience of this impatient man was exhausted.
He drank to excess, and was sometimes legless and when so, he was rude and crude.
He was nearly a midget with a bulbous head ever more revealed by thining hair, an outsized nose with a drinker’s veins in between ears the size of hockey gloves. He had one suit of clothes and when it decayed he bought another of the rack. His clothes were always smeared with cigarette ash for he was a chain smoker; the 2-3 packs a day were what killed him.
Charisma indeed! Whatever it is, he had it. Yet he was not handsome or good looking in any sense. He was not saintly in any way. He did not sound like an oracle. He seldom smiled. Told no jokes. Was no glad-hander or baby kisser.
He was completely indifferent to money. When the police took him in after the manslaughter he had $5 in his pocket. When died he left a bank balance of $2,800. He assigned the royalties of his memoirs to an Inuit trust in his will.
 Daniel Poliquon
Daniel Poliquon
The author’s summation is brilliant. René failed because he succeeded. To explain, he failed in the referenda because he had already succeeded in imbuing Québec and Québécois with the self-confidence to become master of chez nous without sovereignty.
Jules Romains, ‘Men of Goodwill,’ volume 1: ‘The Sixth of October’ and ‘Quinette’s Crime.’
Jules Romains, ‘Men of Goodwill’ is the longest novel ever, running to twenty-seven (27) titles. Yes, 27! They have all but disappeared. Few libraries have the whole set, and finding a set to purchase was a long chase for me. They appeared in an English translation in the 1930s. Each volume contains two novels, apart from the last.
In this, volume 1, there are two novels: ‘The Sixth of October’ and ‘Quinette’s Crime.’

Romains’s description at the start of Paris awakening, stirring, moving on a working day is wonderful. He was a believer in some kind of collective consciousness in crowds and he sees this in patterns, recurrences, and actions and reactions on streets, in the Metro, on buses, in employees clocking in, bicycle riders at a traffic light, trucks backing into loading docks at les Grand Magazins.
Monsieur Quinette spontaneously hides a murderer and involves himself in the crime for no other reason than boredom, and because he is, he thinks, so much smarter than anyone else. He misleads the police, extracts the dosh, but finds Leheuday, the murderer, a thug and a loose cannon. He decides to off Leheuday, nick the dosh, and perhaps take Leheuday’s rather dim girlfriend, while leading the police on a merry dance. Deciding is slow work and his last scenes with Leheuday are interminable. But in the end, bang, bang, and he is dead.
It takes Quinette both volumes to shoot Leheudey who murdered an old women in the opening pages. In another of the several threads started in these opening volumes, the students Jallez and Jerphanion meet and they continue through the remaining volumes I think.
Jalllez and Jerphanion become friends, and the Minister of State Gurau discovers a plot against him. He is another who thinks he is smarter than those around him.
The street scenes are well described. The interior monologues of Quinette and Gurau are well done but they go on too long.
 Jules Romains, who broadcast for De Gaulle from New York.
Jules Romains, who broadcast for De Gaulle from New York.
The whole 27 volumes together comprise an encyclopaedia of Parisienne life — the high and the low. It reads rather like an encyclopdia, earnest, accurate, detailed, and bloodless. Still the characters are differentiated in manner and speech as part of the ethnography of types and the descriptions of Paris are cinemagraphic.
Alan Furst, ‘Red Gold’ (1999)
An espionage thriller from a master story teller who conjures an atmosphere of melancholy from a few lines. Most of the story takes place in grey drizzle with characters who get by on 1500 calories a day, wearing paper thin coats in the unheated rooms of Occupied France in early 1942. They are Jews, bystanders, communists, socialists, citizens, refuges, unionists, journalists who get caught up in each others’ schemes, some petty, some heroic.

The fear, the deprivations bring out the best and worst in people. Pretty Victorine in the travel agency sucks the Jews dry and then turns them in the Gestapo. A gendarme leaves the back door open while he goes to sharpen his pencil and the suspected resistant walks out.
The communists of FTP trust no one, certainly not each other. Students do half-baked, stupid things and get killed. These martyrs inspire others to do more stupid things, and so it goes. German reprisals grow in scale and scope. Life is the one, the only thing that is cheap and readily available.
Grim.
The prose is laconic and spare. In this oppressed world no one has the time for long winded perorations, or for second thoughts. There is no food and hardly any clothing to describe. It meets the Elmore Leonard test. If it is there, then it is important. What is not there is unimportant.

I have read a few of his titles before, but I do find them so melancholic and so grim that there is little pleasure In reading them. It is clear that nothing good is going to happen. And nothing good does.
‘Why Homer matters’ (2014) by Adam Nicholson.
The answer to the title question is in the Iliad:
‘The gods did this and spun the destruction of people
For the sake of the singing of men hereafter.’
Read on for an explanation.
I saw this title on an Amazon recommendation and bought it. My reaction is mixed. I learned something from it, to be sure, and I was reminded of other matters I had forgotten and that is all too the good. I will review some of that before turning to the vinegar in the mix.

The chapters on dating Homer and the Iliad reviewed the debates and evidence I had heard before as an undergraduate but also added a lot to it. Of course there are two issues in dating, one is the composition and the other is the event described in the Iliad. What was new to me here was both ancient and modern. The ancient part were excerpts from other ancient sources who commented on these two dates. The modern was the archeological finds that had not been ratified when I read the Iliad in college, one of which puts Homer himself a thousand years earlier than the received opinion of the 1960s! That reopens the question of the date of war he reported. Was it contemporary or many hundreds of years earlier still?
Then there is the recurrent question of Homer himself. Was he one person at a point in time, or was he several, each commenting on that big Asian land war, or several over time. Or was he the personification of a tradition of epic tales about a single war (or several wars, or a fictional war) in the way a Pop Music could be personified from fragmentary evidence so that a future archeologist might ask where Mr. Pop Music was born, how he managed to be so prolific….
The questions of dating and identity explain the differences between the Iliad with its rigourous hexameters and the varied measures in the Oyssesy, the obvious errors, the gaps, and the repetitions. One sample suffices, in the Iliad a named warrior is killed, his death detailed. Then a few score lines later he is back in battle! Homer nods, was the tag line.
The author does answer the title question although I am not sure he realises it when he quotes the lines above from the Iliad:
‘The gods did this and spun the destruction of people
For the sake of the singing of men hereafter.’
To explain, the gods led the men into this war to create events worthy of an epic poem of the magnitude and grandeur of the Iliad. Wars there were many, cattle raids, clan vendettas, boundary disputes over grazing land, pirate raids to rape and pillage in a day or two, involving this tribe, that village, a Kingdom here or there. But the scope of the Iliad adds all of those up and doubles it. Greeks from Ithaca on the Adriatic Sea to the Peloponnese, to Euboea in the Aegean Sea come together in a massive expedition. Jason had one ship and became legend. Here were a hundred ships to make an epic. None of these men would have been remembered but for the war, well, not quite, but for the poet who afterwards made the war and them memorable.

Art is life and the purpose of life is art. That is what we learn from Homer. Without art to capture, articulate, crystalize, preserve, and communicate life we are sheep in the field who leave nothing behind but dung and bones. When the flesh is gone, the poetry remains. That is Homer’s deepest meaning.
It is part of the genius of the Iliad is that it incorporates dissent, when the most enduringly famous warrior, the man at the centre of the Iliad, Achilles says he regrets it all. Famed as a warrior, slayer of men, many men, raper of women, many women, this same Achilles loved Briseis, loved Patroclus even more, weeps in the arms of Priam. This man of men is also a lover and loser. Fated, he knows. A preternatural warrior and an immature human being.
There were some omissions from the book, the foremost is some greater explanation of the origins of the texts we have. Does the Penguin Iliad trace back to…a complete Greek text on Egyptian papyrus? Is it the same original text that underlay Mathew Arnold’s Iliad two hundred years ago? When and how did Homer come to medieval Europe? Was he a travelling companion of Plato and Aristotle when Lorenzo Medici commissioned Latin translation from Greek masterworks then known in Europe only by references in extent Roman works. Plato and Aristotle we know did not exist in complete Greek texts but rather in Arabic translations that had survived and then a thousand years later were back translated into New Testament Greek. Without a doubt there were errors in translation. What was Homer’s path?
There is too much ME in the book. No doubt this personal element is an asset to some readers but not to this one. Knowing that the author thought of a passage from the Iliad when climbing the steps at…adds nothing and takes attention from the subject. There is a lot of this. Some has a thin justification in that he went to some of the places in Homer’s books, but even so, who cares these millennia later. He is no Homer. Moreover, he did not go to the obvious place, Troy and makes no comment on it. By the way, reopening the dates as mentioned above might mean Heinrich Schliemann was right about which layer at the site was the Homeric one!
I also found the comparisons to other Bronze Age people a long bow, and likewise the comparison of the Greeks at Troy to twentieth Century gang behaviour tenuous and tendentious. It filled the pages which I went over lightly, very without learning anything.
 Adam Nicolson
Adam Nicolson
Many of the Bronze Age comparisons do not apply to the cosmopolitan, urban, artistically rich Trojans, and Nicholoson says that and then ignores it at other times. He generalises about Homer as though the Trojans were not there. Yet one of the beauties of the Iliad is that the poet does not take sides. Priam is majestic; Hector is noble; Andromache is stoic. These are the losers, the Asians. In contrast Agammenon is grasping; Achilles petulant; and Odyseuss is lazy. These are the winning Greeks, and no PhD has ever disputed that Homer was Greek and on the Greek side in some sense.
Stylistic irritations include direct address ‘you’ which I find distracting, a faux familiarity, and informal where the rigour of formality is the best support for exposition. There also seem to be some liberties taken or are they simple prejudices as when he gratuitously refers to ‘the sterilities of Oakland California’ on p. 74. There a few of these, shall we say, Bill Brysonisms: snide and superfluous remarks.
There are extensive notes but I rather think they were selected for fit not after analysis. There follows a long bibliography. I thank the author for both since I suppose it took a fight with the publisher to include these extras. That said, I judge them to be window dressing, not substance.
‘King O’Malley: “The American Bounder”’ (1981) by Arthur R. Hoyle
A biography of KOM, as he was sometimes called. A Canadian, a Kansan, a Quebecker, a New Yorker, depending on which lie he was telling at the time. O’Malley (1854-1953) spent 65 years in Australia in Hobart, Launceston, Melbourne, Perth, Sydney, and Adelaide. Often one step ahead of bailiffs. Indeed taking ship to Australia in the first place may well have been to evade creditors when he was about 25 years old.
 The man himself, King O’Malley
The man himself, King O’Malley
To establish himself with audiences here and there he claimed a variety of backgrounds and motivations, uninhibited by what he had said previously elsewhere to other audiences, and there was no social media to trip him up. So convincing a liar was he that he convinced himself, repeatedly. And audiences he had to have. He was a man who craved attention, and found it to in sound of his own voice. He looked and sounded American to his contemporaries in Australia, but he claimed Canadian birth to qualify for citizenship and a run at parliament, first in South Australia, and then in Canberra.
He started out selling insurance but discovered, as have others like Huey Long, that the product he could best sell was himself.
Loud, brazen, boastful, egotistical, obnoxious, he was just like all Americans in the Australian stereotype today. So thought many then but more fool them because voters elected him. His political career started in South Australia, borne, said his foes, on the votes of women who found him a handsome and dynamic man. So much for Enlightenment Adelaide. Having sold insurance most of his life made him — in his own mind — a financial expert, that plus the United States had a national bank were enough to convince him of the need for national bank in Australia. It was a theme he played throughout his political career and in the end he was one of the driving forces in creating the both the Commonwealth Bank and also the Reserve Bank of Australia. There were many objections to both.
Physics is so simple, as Isaac Newton said, for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. In politics for every action there is a myriad of diverse reactions that roll on and feed on themselves. Together they far exceed the original action, and they go off in so many directions that they cannot be tracked.
While he advocated many causes on the nascent Labour agenda at the end of the 19th Century, he was reluctant to join that party and accept the discipline that went with it. Round the turn of the 20th Century the party system did not have a deadlock on seats, and there were a number of independents. Nonetheless, he supposed he would get a cabinet seat. Someone had to tell him to join that club he had to join the party club and he became a Labor man. His constituency was Darwin in Northwest Tasmania though he lived in Melbourne in the main.
He was minister for home affairs in two governments where he seems to have made a point of clashing with the officials in the Department. Accordingly there was a great deal of smoke and lightning, but the snail’s pace continued.
Because he was a rootless bounder, he had traveled far and wide in Australia selling insurance for years before entering politics. Consequently he had seen more of the country most of his colleagues and that led him to advocate a national railroad. Another theme he stayed with for years.
Perhaps his most lasting mark on Australian was to support Walter and Marion Griffin’s design for Canberra, and to stand by that design and the Griffins when the political football game began. There were many ups and downs but they remained friends so that in his 60s and out of politics when O’Malley paid his only return visit to the United States he stayed several weeks with Walter’s parents in Elmhurst near Chicago.
 O’Malley at the ceremony inaugurating the site of Canberra
O’Malley at the ceremony inaugurating the site of Canberra
As O’Malley aged he matured. Many of the passages quoted from Hansard on the bank, the railroad, or Canberra as far less bombastic and more reasoned than his comments on the same subjects twenty years earlier.
By the way, he was a teetotaller all his life, though he freely bought drinks for others, clients and voters. Yet there is pub in Civic in downtown Canberra that bears his name on the stereotype that all Irish are sots. When travelling he never stayed at a licensed hotel such was his aversion to drink and drinkers.
 The pub in Civic
The pub in Civic
He was personally frugal to a fault with his own money and that of the Commonwealth. Religion is not mentioned. King was his mother’s maiden name. He spent about twenty-five years in retirement burnishing his reputation. He married Amy in his 40s and they stayed married, though our author speculates that King was not a romantic. Having bought property whenever he could along the way, he was a wealthy man and he arranged for his estate to support scholarships for girls only. In the 1960s a Canberra suburban was named after him.
This short book is judicious and droll. It should be of interest to anyone who has wondered about Canberra came to be as it is. It faithfully recounts O’Malley’s words and deeds and then slowly applies a great deal of salt to arrive at conclusions. It is far more circumspect than the credulous entry in Wikipedia. Likewise the entry in the ‘Australian National Dictionary’ of biography is very cautious.
‘The Crag’ by Wendy Spathopoulos (2007).
The ‘Crag’ is Castlecrag on Middle Harbour, Sydney, a jewel hidden in plain sight on a peninsula, there are no through roads and so no passing traffic. Thus it is not known to many locals, despite its rich, even unique, history.
It has two distinctions. First, it is one of the last places in metropolitan Sydney that Aboriginals lived in their traditional way into the 1920s. There is photograph evidence of that in the Mitchell Library archives on Macquarie Street. Second, it was home to Walter Burly Griffin and Marion Mahoney Griffin, who created Canberra, the national capital, for more than a decade. This latter is the focus of the book under review.
The location, planning, and building of Canberra was a very large and lucrative political football, which was kicked and pulled in all directions. The main point relevant here is that there was an international design competition to plan Canberra, and the entry chosen by the selection committee had been submitted by Walter Burley Griffin of Chicago who worked with Frank Lloyd Wright, as did Griffin’s wife Marion. Walter and Marion migrated to Australia to contribute to the building of Canberra, setting up headquarters in Melbourne in Chinatown.
In short order a kick of the political football tossed Walter and Marion off the project, though the overall conception remained theirs, as did the eponymous lake when it was finally built (does one built a lake?) in 1961, fifty years later.
They had established an architectural practice in Melbourne and occasionally visited Sydney to meet clients. At some point they saw the wilds of Castlecrag and decided to move there. They set up a business to develop the Crag in accordance with their own planning and architectural principles, designing and building houses, parks, an amphitheatre, an incinerator, and a hospital.
In 1926 when Canberra was declared open for business in a grand ceremony, the Griffins were not invited. That will sound familiar to many who have toiled in large organisations with neither corporate memory nor simple courtesy but replete with strategic plans and a branding campaign…..

Wendy Spathopoulos summarizes the story above, but concentrates on the Crag years, which she witnessed as a child. She writes very well, strikes a balanced tone, and offers the results of library research, archival burrowing, interviews, and personal recollections. It is a mixture, to be sure, but she pulls it together well. Stories of colourful characters, and none were more colourful than Marion Mahoney, are mixed with the dreary struggle to get planning approval to build a house with the kitchen at the front near the street, and not at the back. Yes, Ripley, the Willoughby Council fought this to the end. Kitchens have always gone in that back and in the back they should remain. However, there was no legal grounds for this imperative and in the end, the Griffins prevailed.
By the way, they put the kitchen at the front so that deliveries from the street could be done easily; think of those times you have carried groceries through the house to the kitchen, and the point is made. In addition, putting the kitchen at the front meant the wife, inevitably at the time, had ready access to the street for child minding, for seeing neighbours, for reducing the social isolation of the wife at home.
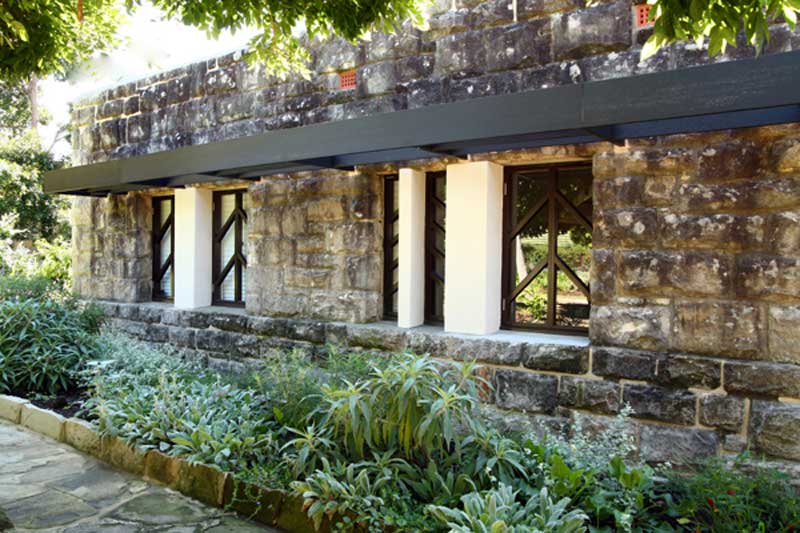

The Griffins’ principles of design emphasised integration into the natural environment, per Lloyd Wight, and maximum functionality of space, including the roofs, which were flat for use in drying clothes, and as a patio. This also threw the Willoughby Council into hysterics, to judge by the minutes of meetings quoted in this book. Flat roofs were … unheard of, safety risks, a health risk, the work of Satan. But again there was no legal basis for the reaction and with persistence it yielded, but it shows that nearly every step was uphill.

It was all uphill in another sense, too, because Castlecrag is a ridge line with steep slopes on both sides down to Middle Harbour, and that pushed up building costs, though it kept down land prices. But by following the contour of the land, the Griffins tried to keep the cost of road building down, but once again Willoughby Council objected. Roads had to be straight, even if nature was not. Take it as read that Willoughby Council objected at each and every step to each and every thing.
The houses were small so as to be affordable, two bedrooms, with small rooms to economise on heating and lighting costs, with many large widows and serving ports to ease the work of the wife in the kitchen and walk through fireplaces that could heat two rooms. Yes, the Council objected to most of these design elements as well.

Marion Mahoney was larger than life and a dedicated amateur thespian. Hence the amphitheatre for the neighbourhood productions she orchestrated. She involved the local children in preparing the sets, props, costumes, and performing in some of the works where suitable. She and Walter knew many artists from Melbourne, some from Chicago and met more in Sydney. The players were amateurs but the productions were not amateurish. Marion designed and built the sets, as well as the costumes and props. The plays she produced included:
A Midsummer night’s dream – Shakespeare
Iphigenia in Tauris – Euripides
Prometheus bound – Aeschylus
The Green snake – Goethe
Oedipus Coloneus – Sophocles
In keeping with their commitment to the integrity of the environment, the Griffins spent a lot of time on storm water re-use — yup, another bone of contention, sanitation, and sewage. He designed his own sewer pipes because he found the Council standard inadequate. Guess what?
Spathopoulos describes both the Griffins as energetic, optimistic, and vital. The resistance of the Willoughby Council presented an opportunity to educate its members in design principles, building techniques, the value of social interaction, the integrity of nature, and so on. Thick skinned indeed these two paragons. However, banks were altogether harder since they did not hold public hearings. Banks? Yes, the banks were unwilling to lend money to buy such oddities as the houses the Griffins designed and built.
Walter also devised his own construction techniques and manufactured the building blocks to do it. Once again resistance was futile, if exhausting. He did not only design and plan, he also built and often pitched in on the manual labor. Marion was a keen gardner throughout the area, always native plants. Super-Greens avant le mot, they never uprooted a tree to build a house but planned the houses around the existing trees. Guess how the Council reacted to that.
Walter and Marion were keen connoisseurs of the many varieties of eucalyptus trees, and would have loved the novel ‘Eucalyptus’ (1999) by Murray Bail, I know I did; it is reviewed elsewhere on this blog. Walter taught the local children to identify the varieties of the gum tree with their Latin names.

While artists, some university people, a doctor or two bought Griffins houses in Castlecrag, they were few, and then the Great Depression came. King O’Malley, that giant of Canberra politics, remained a lifelong supporter and friend, bought a house as an investment. So did two Chinese the Griffins had gotten to know in Melbourne. Miles Franklin, the writer, was a frequent visitor but could not generate the finance to buy, and no bank would lend to a woman in those days. (Indeed about every 15 years there is a review into banking in Australia that discovers it is still true that banks are very reluctant to lend to women.)
Despite some trials, the Griffins prospered in Castlecrag, ever active and creative. They were active in the Theosophical Society and later the Anthroposophical Society, both forms of occult spiritualism which were in vogue at the time. There were one or two trips back to the States. He went to India on a commission and found much work there, and Marion joined him for a time. He died there and she returned to Castlecrag for a while.
Utopian theory and practice led me to planned cities, and I tried for years to interest a student in a thesis on that subject. Brasilia, New Delhi, Washington, Canberra, they offer plenty of choice. Hence I have read about Canberra and Griffins and saw in them a dotted line back to William Morris and one thread in utopia.
I put a visit to Castlecrag on the To Do list, and one day its number came up. There is a guided tour offered by the local residents association, on which I commented in an earlier post, and off we went. At that time I came across this title, but found it was unavailable and not in the University library. I put it on my Amazon Wish List and one day I noticed it was available and acquired it. It runs to 400 pages and has many photographs included. Too bad it is not more widely and easily available.
The book is unpretentious, straightforward, and lets story speak for itself, but I found the author’s decision to intersperse chapters about a visit to Greece distracting without adding to story of Castlecrag.
Your tax dollars work, published with an Arts Council grant.
Frederick Lieb, ‘Connie Mack: Grand old man of baseball’ (1945)
I was looking for a biography of Mr. Mack (1862-1956) and this is as close as I could get and it is not a biography. Apart from a couple of early chapters about his playing career, it charts the seasons of the Philadelphia Athletics to 1945. It bursts with baseball clichés and brings back to mind some of the famous names, but there are no insights. Mack managed the Philadelphia Athletics from year zero 1901 to 1950, more than 7,000 games.

There is nothing about Mack’s ability to manage his teams, the more so as he aged and the players got richer. That was what I was looking for. I did learn why the name ‘Athletics’ and why the ‘White Elephant’ as a mascot. Members of the Philadelphia Athletic Club were the early investors at the turn of the Twentieth Century. It was a racket club. Skeptics said the franchise would be a white elephant, i.e., not succeed, and Mack and Shibe, the major shareholder, took that as the mascot image. They added the baseball either as a conscious reference to fickle fortune, as balancing on a ball symbolised in the Renaissance, or just because it was a baseball!

Mack played professional baseball from 1886 to 1896 and shifted into coaching and managing. He proved adept at managing some pretty wild and undisciplined characters, but how he learned to do this and how he did it, are not to be found in these pages. He also learned to treat management as a business, being himself part owner of the team.
In the unregulated era that covered most of his seasons, poaching players was common, rival teams would set up across the street to siphon off fans, journalists were unscrupulous, and many players found the money had to be spent on alcohol and women. Somehow this man who himself did not smoke, drink, or swear convinced most of his players to follow his example. Those he could not win over, he let go. By the way, that is the origin of the name Pirates for Pittsburgh, because it pirated players from other teams when it had steel money.
Shibe park was mostly .25 cent bleacher seats to allow its working class fans to attend, and the attendance gate was the only source of revenue then. Accordingly the Athletics could never compete with the New York and Chicago teams in money.
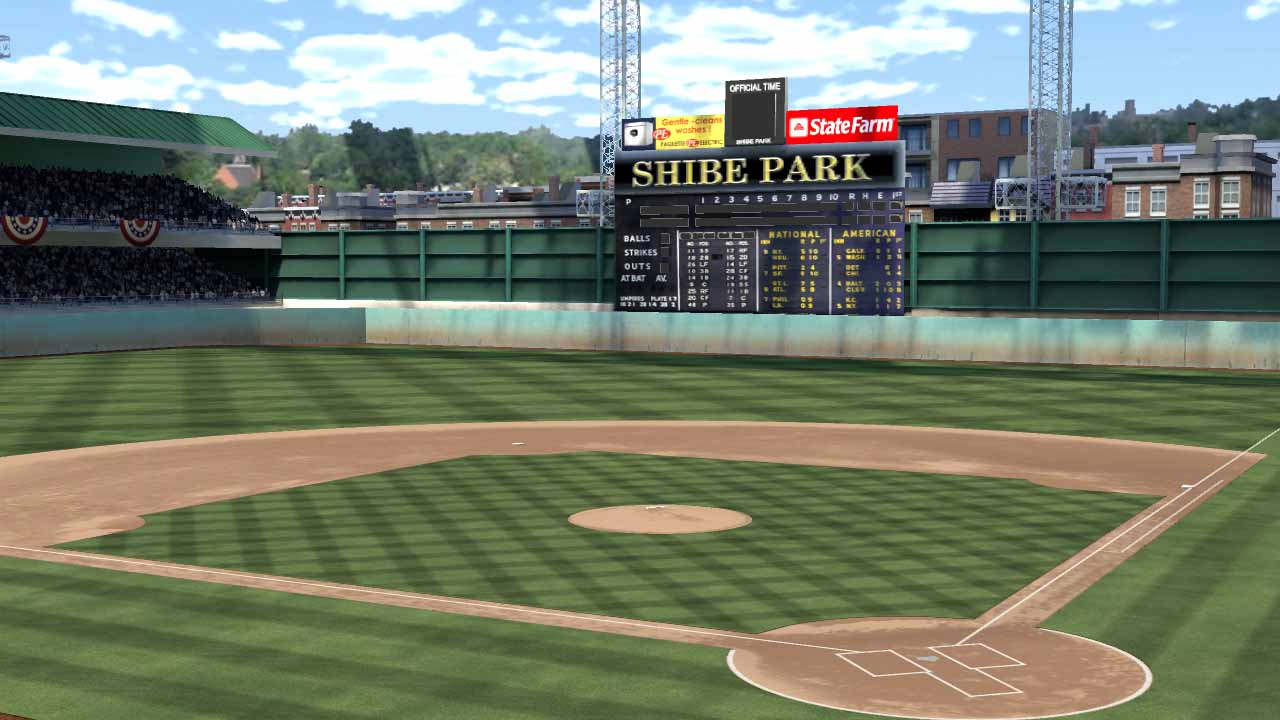 Shibe Park, interior.
Shibe Park, interior.
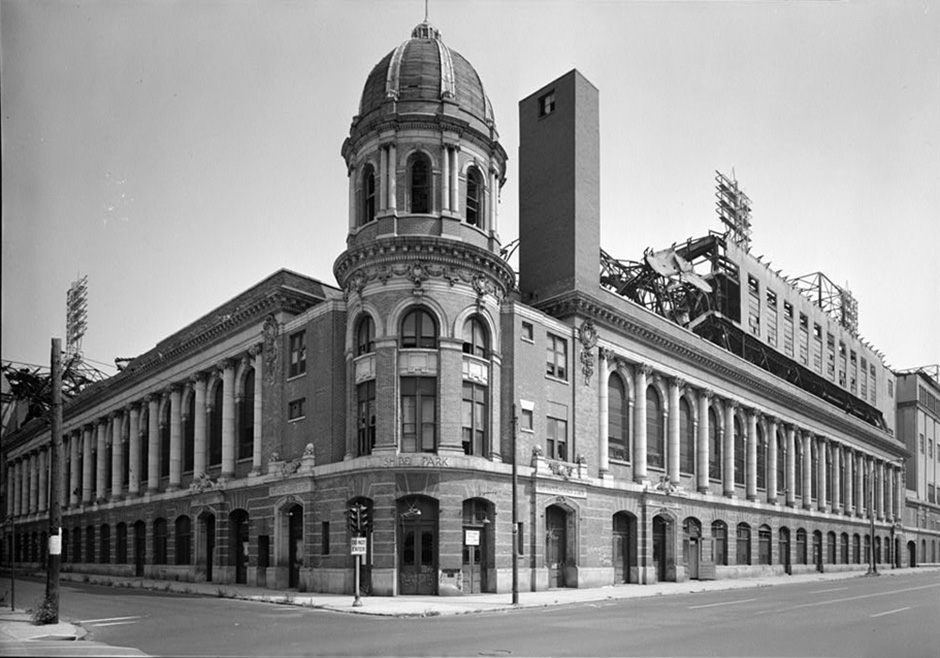 Shibe Park, Street view. Mack’s office was in the tower.
Shibe Park, Street view. Mack’s office was in the tower.
One of the distinctive feature of Mack was that he always wore a business suit when he managed. There he is on the dugout bench in a suit, tie, and hat with his players, scorecard in hand. Earlier in his career as a manager, before the A’s, he had dressed with the players and changed back into street clothes with them, as is still the norm in baseball. He stopped doing it because he found it hard to control himself, he told the author, sometimes after a stupid loss. He decided to stay out of the dressing room altogether, leaving the coaches to that realm, and establish some distance. Then when the wanted to talk to a player about that stupid loss, he would do so later that night in the hotel on the road, on the next day before the game, but in each case privately when cooler heads prevailed all around.
 He became a national figure.
He became a national figure.
Of course the most impressive thing about Mack, and it comes through in this book, is abiding enthusiasm and interest in the game, its rules, its players, its symbolism, its continuity for more than fifty (50) years.
‘Elizabeth I Renaissance Prince’ (2014) by Lisa Hilton
The title caught my eye. The juxtaposition of ‘Renaissance’ and ‘prince’ had to mean Machiavelli, so it did. I thought to read it then, to find out how Machiavelli is maligned within and, after all, Elizabeth is another great leader per my presidential reading project. So off I went.

My head whirled at the time and place. What a world was the Tudor court. What a time in the continuing bloody conflict between staunch Catholic and zealous Protestant. This was not a polite doctrinal dispute but one that often ended, quickly, at the end of an axe or pyre for burning dissents alive as soon as possible.
In reading all of this I am reminded again that Henry VIII had very good political reasons for his six wives. Now it is true that the women he selected sometimes were chosen for sexual attraction, but he desperately needed an heir. And that heir would have a better chance of support and survival if it was a he and that he was a Protestant. That he had six wives was a measure of the desperation for an heir as much an anything else, contrary to the vulgarians on the idiot box who can think only of genitalia, telling us some much more about themselves than Henry.
I learned a few things, against the odds as explained below under vinegar. Elizabeth’s half-sister Mary Tudor, who ruled for five years as Mary I of England, is not Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots, though the confusion is invited because Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots, was styled Mary I of Scotland and since there were those who thought she ought to be on the English throne, she was sometimes thus referred to as Mary I of England, too. These two Marys were cousins of some remove. Mary Stuart, Queen of Scots, descended from Henry VII (father of Henry VIII). Henry VIII was father to both Mary Tudor with Katherine of Aragon and Elizabeth Tudor with Ann Boleyn. Mary was 15 years older than Elizabeth. Neither had anything like a normal childhood.
Elizabeth Tudor, as a child, survived the court intrigues in part because she was a girl and so not considered a threat by any of the court factions. Her younger brother, Edward was the presumptive heir and attention focussed on him. At one time or another, Henry VIII, while he still lived; Edward VI, the boy king; Lady Jane Grey, and Mary I either disinherited or denounced Elizabeth. By disinherited I mean excluded her from royal succession. Sometimes this exclusion was done though an act of parliament, and at other times by a decree. Then there would occur a shift in court politics, or a rumble in European affairs and restoring Elizabeth seemed politic.
Edward VI was the first king raised and educated into Protestantism as was Elizabeth, and the first monarch to come to the throne a Protestant. MaryTudor, the older sibling, was reared by her mother, the very pious Spaniard, Katherine, into Iberian Catholicism, that of the Inquisition. If there were variations in Catholicism, this was the take-no-prisoners version. The best way to save the soul of sinners is to kill them immediately to stop the sin, and make things easier for them in the afterlife. If that sounds wacko, read more about the Tea Party to find contemporary parallels.
The boy King Edward was never robust and on his deathbed at 15, he signed a paper passing the crown onto Lady Jane Grey, who had reared him and nursed him in his last days, his mother, Jane Seymour, had died in his birth. Whether Edward knew what he is doing or not when he signed, there were many who supposed the crown was not his to give, and Lady Jane Grey’s interregnum lasted 9 days. To save herself, though very Protestant, she professed allegiance to Mary. It did not save her.
Mary Tudor became Mary I for five years. She pulled off a diplomatic coup with a political marriage to Phillip of Spain, heir to the Castilian throne. Phillip spend a year in London where he counselled her to show moderation to Protestants. Though very much a Catholic himself, the point of the marriage was to secure a powerful English ally against the French. That would not work if the English turned against each other in a religious war. Being a seaman himself, he also introduced reforms into the Royal Navy in ship building and in promotions. Ironic, no? This is the same Phillip who dispatched the fabled Armanda against the Royal Navy he had helped create while Elizabeth, the women he shielded, was queen.
Matrimonial politics makes strange bed fellows, for while the conjugal alliance with Phillip of Spain corralled the French for a time, it was not popular with the English public, nor with the many nobles who preferred one of their own in that bed. Even English Catholics were less than enthusiastic for a Spanish king. Note, he was accorded the ceremonial title king, but the marriage contract specifically denied him any authority, but still there was that word ‘King.’
Elizabeth bent to Mary’s will, even proclaiming herself a good Catholic in a letter. Mary did not believe the profession but it was enough to paper over the differences. There were Protestant plots to do away with Mary and they turned their eyes to Elizabeth as a figurehead. She can hardly have failed to know this, but some how kept a distance from it. When one such plot was revealed, Mary sharpened an axe for Elizabeth’s neck, but Phillip urged restraint. Why? He had a second reason. Mary Stuart that Queen of the Scots was the other most credible claimant to the English throne and she was betrothed to the French King. If Mary Tudor I were to die, and Elizabeth was dead, that would make Mary Stuart, Queen of the Scots, the inside favourite for London, thereby undoing the English-Spanish alliance he had devoted himself to securing. So Elizabeth lived, and that kept Protestant hopes alive, as well.
Then Mary succumbed in an influenza epidemic and there was no one else but Elizabeth for the Protestants. While the author stresses Elizabeth’s solid education, linguistic ability, honed survival instinct, it must also have been the case that there chancers around who hoped to manipulate and use this girl-queen, just as such men, including members of the Grey family, who manipulated Edward VI.
Be that as it may, Elizabeth did everything possible in word and deed to emphasise the smooth continuity of Tudor monarchs from Henry VIII, Edward VII, Mary I to Elizabeth I. While the most Catholic elements of Mary’s rule were set aside, some was preserved in a gesture of moderation. Though it was never enough either way. The Catholics wanted a Catholic queen and all the Protestants put to the sword, and the Protestants reciprocated.
 Mary Stuart
Mary Stuart
Elizabeth’s reign was long, and domestic, national, and international politics swirled around in admixtures. She flirted with men, but found having suitors secured a kind of stability, rather like Penelope and that weaving. Mary Stuart kept plotting and finally was entrapped, and went to the stump. Many others went, too. Yet no one uses Elizabeth’s name as a shorthand for murderousness. Odd that. Of course, Henry VIII oversaw the slaughter of more than 50,000 Catholics who were his subjects and his royal oath pledged him to protect and defend his subjects. Hmmm.
Francis Walsingham created MI5 and MI6 in all but name, and ferreted out plotters, and no doubt fomented some of them to justify an increased security budget.
When Calvinist rebels who attacked the Spanish in the Netherlands appealed to Elizabeth for help, she being the leading Protestant monarch in Europe, the other major one was in Sweden, Elizabeth gave just enough help to keep the Spanish tied down in the Netherlands, but never enough to bring about a decisive result. Better to have Spain tied down in the Netherlands than to have it freed from that need by a decisive Calvinist victory. Who said ‘cynical’?
There were many approaches of marriage both international and national. In light of the popular reaction to Mary Tudor’s marriage to Phillip, there was no chance of a foreign husband, but let the suitors come… In time the Virign Queen used that claim to identify herself with both the Madonna, and with England as her immaculate child. The author goes into the symbolism of this at length, the jewellery, the portraits, the gild.
But the point remains that there was no heir. That must have bothered a lot of people who could foresee a gathering of the carrion when she died. And she could have died at any time, falling down stairs, in an influenza epidemic, by tetanus from a small cut, bad water while travelling, the list goes on. Those who supported her the most, these had the most to lose if instability followed her death. They must surely have thought about this, and they must surely have taken out insurance of some kind. The author reveals nothing of this.
The one chapter where the author does dig concerns Elizabeth’s speech at Tilbury when the Spanish Armada was approaching.
 That armada.
That armada.
Hilton concludes, mostly by assertion, that Elizabeth did not give the speech widely attributed to her (See William Safire, ‘Lend me your ears’). That she went to Tilbury to consult with the admirals and generals is documented, but not that she spoke or what she said if she spoke. The author concludes the speech was retrospectively credited to her a generation later, and stuck. I do like that kind of digging, though I was disappointed at the conclusion, but it seemed to rest largely on the absence of evidence, and as Donald Rumsfeld taught us, the absence of evidence is not evidence of absence.
Oh yes, Machiavelli is mentioned several times and is shown in one of the coloured plates in this handsomely produced book. The mentions are gratuitous and superficial. Par for the course.
Lisa Hilton is a successful author with many titles to her credit. The back cover of this tome bears this blurb: ‘Game-changing…how history should be written,’ Andrew Roberts. I expect this the Roberts with a lengthy and laudatory entry in Wikipedia where he is described as a British historian and journalist, and a FRSA and FRSL, dignities so far above my station that I know not what they are. Yet I dare to dissent.
The experience of reading this book was like watching squeal televisions programs, where gangs of immature adolescents shriek and squeal at each others’ dresses, make-up, hot-rods, guns, and general vulgarity. It is my first squeal and shriek book. Much more attention is lavished on the gowns, the regalia, the jewels, than on the forces in play that lead to the events at which the gowns are worn. It might also be compared to one of those celebrity magazines I pass by at supermarket tills, combining glitz and gossip a mile wide and an inch deep.
The book starts in the middle; is breathless throughout; opinionated without being informative. It makes no concessions to the reader’s desire for an orderly exposition of the facts of Elizabeth’s life. Instead it replicates the kaleidoscope of the times in blizzards of name-dropping, as if all readers already know all of this and are waiting for the writer to tell us what to think. She does tell us often with that dreadful adverbs: obviously, reasonably, rightly, finally.
I made my own chart of the principal characters so I could follow, to some degree, our breathless correspondent as she darts from one subject to another, seldom leaving a transition, internal summary, or any other signpost behind. What would Jacques Barzun say about this? Probably not that it is how history should be written.
That there is contention over facts or interpretations is taken as license by this writer, not as a matter that requires careful adjudication. There is little evidence in the text of the impact of studying the lengthy bibliography at the back. It is rather as the script writers say: based on a true story. Sometimes passages in quotation marks have a footnote and sometimes they do not. The footnotes are often to whole books, and not to passages, page, or specific points.
 Lisa Hilton
Lisa Hilton
‘What he was accused of compassing was the possession of two Tudors, the king as his charge and Elizabeth as his wife.’ Huh? ‘Compassing’? It has an archaic meaning as ‘contriving’ but really, how many 21st Century readers will get it? I did not. This is one example of many instances where odd words, usually long, are used. All those students I have read who thought big word was a big idea, they came to mind.
Elektra/Orestes at the Belvoir
A one hour summation of the blood bath in the house of Atreus.
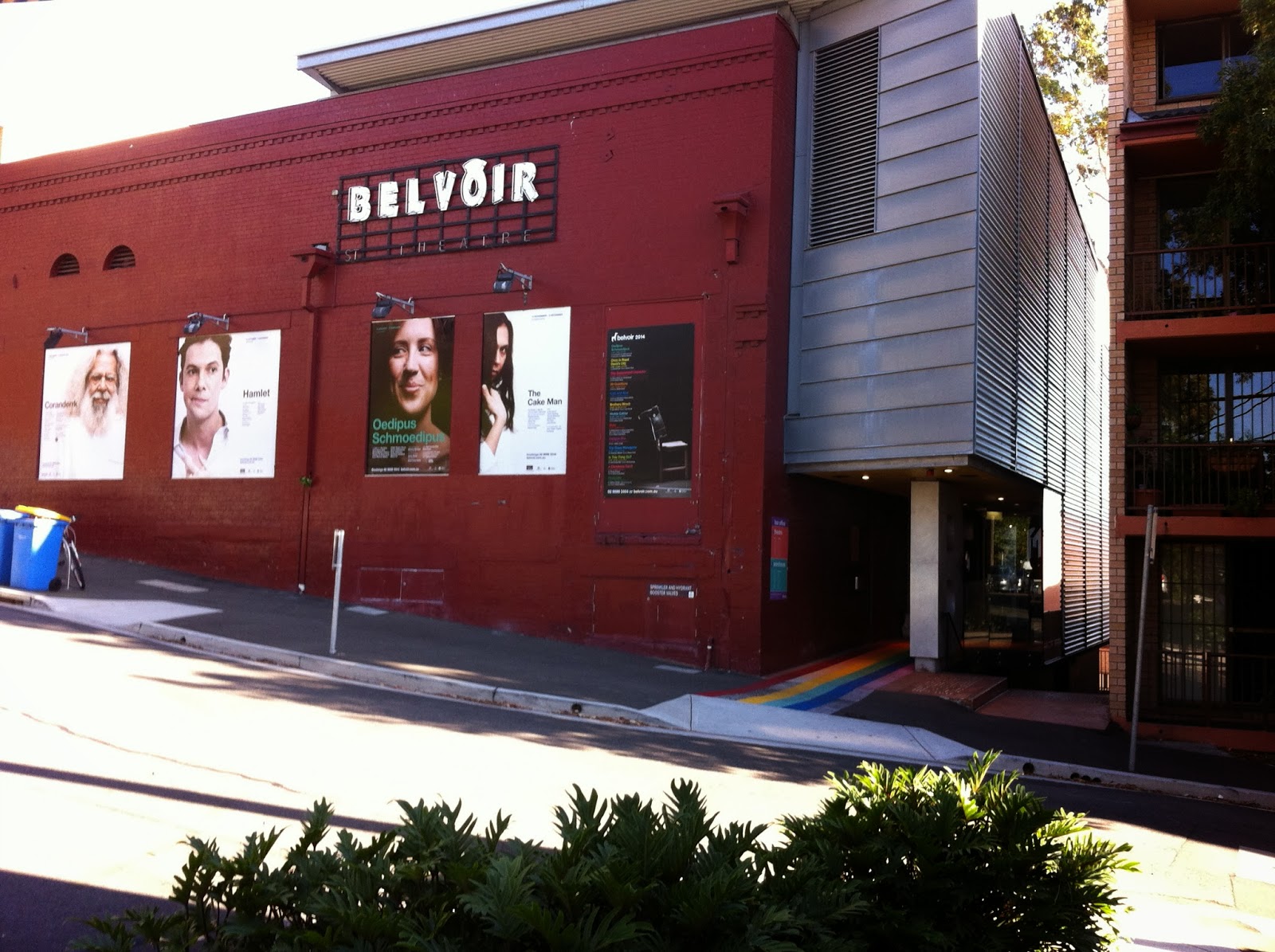

Brilliantly staged with a committed cast it takes many liberties with Euripides and updates it to the IKEA age.

This Elektra is a petulant, overgrown teenager who sulks and makes a great deal of noise. There is in her no sense of impending doom or menace. She has spent eight years not growing up and seems bound to go on that way indefinitely. Though Elektra had to carry the emotional core from the get-go.

The intensity in the original is lost here in a blizzard of the F word. Nor did any of the famous lines from the original make the transition.
Vengeance in this rendering is reduced to filial love, but in any of the Greek versions there is far more at stake than that. Since the murder of Agamemnon the land has been cursed, no rain, goats born with two hears…. The natives are indeed restless, believing the gods have condemned the land and all who there dwell because of the murder of the king. The gods must be satisfied, yet the only way to satisfy the gods is with another unrighteous murder, that of Clytemnestra and her paramour. Indeed in the Greek versions, while the deed is done, it does not atone, for that Elektra and Orestes have to leave…. pursued by the Furies, but in so doing they draw the curse off the land. If tragedy has no-winner, then this is tragedy.
These quibbles aside, it was compelling and the overall theme of the story remains.
I particularly liked the insouciant Aegisthus with his worn bathrobe. Just right. Though it took him a long time to die and it began to seem as though Orestes was counting the stabs to reach a set number. I suppose the number of blows was intended to look like a frenzied attack but it did not; rather it looked methodical, and pointless.
But the overall staging was memorable, go see it for yourself to see why.
