Now and again I have had the urge to go to Venice, but never have. To scratch that itch I decided to read a history of the damp republic.

A fishing village on the lagoon is first mentioned in extant chronicles at about 800 A.D. Venice was not a Roman settlement, unlike nearly every other city in Italy today. The mud flats in the lagoon were home to fisher folk who were left alone by others because there was nothing there worth having or worth stealing.
From this embryo grew a mighty city that dominated much of its world for three centuries.

The constant threat of the sea, aqua alta, meant everyone in Venice had to cooperate against nature. That common and constant threat produced a tight social order that put an absolute premium on planning, discipline, and initiative, and most important of all on social cooperation both horizontal and vertical. The commune took precedence over the individual and orders were obeyed.
This is my reading of it because the book is mainly focused on the wars of conquest and decline that led to the empire and then its collapse.
While most European cities between 1200 and 1500 developed an increasingly elaborate hierarchy based on blood, money, and religion, by contrast Venice remained largely undifferentiated with a very flat social hierarchy. That proved a bedrock beneath the water. In this way it seems to me that Venice is comparable to that other muddy republic that lived off trade and battled the sea, Amsterdam. See Geert Mak, ‘Amsterdam’ (2001).
The people of the lagoon had almost no terra firma. That was a benefit since it meant no passing war lord wanted to wade out into the mud to conquer it. It was also a weakness since it meant Venice had to live off trade because there was no vegetable patch. It had to be the broker to live.
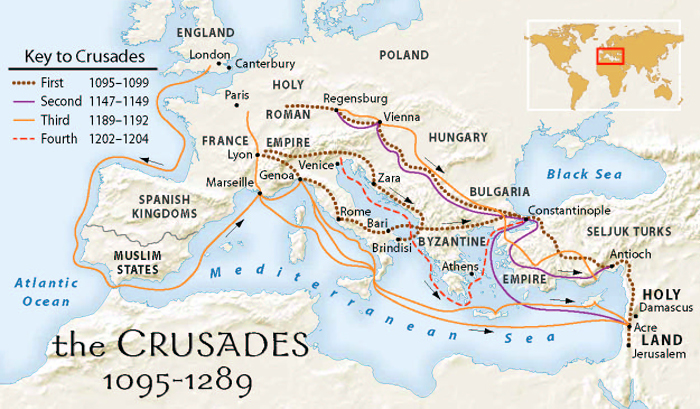
Its conversion from a diet of fish to one of gold began with the Fourth Crusade in 1200 which occupies the first one hundred pages of this book. It is a story for the ages.
The crusades were religious, the aim being to wrest the Holy Land from the infidel, and all those who participated in the effort would be blessed in the Christian heaven for eternity. Sounds like a Holy war because it was.
The first three crusades had limited successes and unlimited failures. They left behind Christian enclaves in the Middle East. Of course, the largest Christian community in the Middle East, as we call it today, were the Greek orthodox Christians in Constantinople. The author refers to that city of the Bosphorus by that name, though at the time it called itself New Rome.
The endless religious schisms in the preceding millennium had divided the Christian world into these poles: the Universal Church in Rome and the Greek Orthodox Church in New Rome. The twain did not meet. At each pole there were further divisions: Two fingers versus three fingers, is one example. (Either one gets it or one does not.)
The Byzantine Empire in New Rome had participated in the earlier crusades, but not as fervently as Popes in Rome thought it should have done. This was another source of friction in the Christian world.
When Saracen leaders in Syria began to squeeze the pimples of the Christian enclaves in Lebanon, the Roman Pope called for a Fourth Crusade to rescue them and to conquer the Holy Land once and for all.
Whereas the earlier crusades had been more or less spontaneous movements of mobs of Christians from Europe to the Holy Land by any and all means, motivated as much by the selfish desire to save their individual souls as to cleanse the Holy Land of Islam in a rag-tag mob of inexperienced, impoverished, undisciplined and diseased hordes who were often unarmed, this crusade was different. The Pope made an effort to organise the Fourth Crusade. by commissioning a number of nobles to lead and manage it.
The plan called for thirty thousand crusaders to be raised, equipped, provisioned, supplied, organised, and assembled in Venice, from whence Venetian ships would transport them to Tyre, Sidon, Beirut, and other ports along the coast of the Middle East. This crusader army would be commanded by Christian lords, barons, and knights from the lands of France, Germany, Italy, and Poland, by and large, though others joined the cause.
An advance party went to Venice to prepare the way. There its members discovered that the Venetians expected to be paid in coin for shipping these souls to the desert. Long and difficult negotiations followed. While Venice had dabbled in sea trade for its living, this project was a hundred times larger than anything previously undertaken. To transport thirty thousand men in a single fleet, along with their arms, equipment, and food, was such a difference in degree from previous trade expedition as to be a difference in kind. Furthermore, a knight must have his steed, and some five thousand horses with grooms, squires, tack, fodder, and more had to be shipped at the same time. Hundreds of ships would be required and thousands of crewmen not he oars and sails.
The Crusaders agreed, reluctantly, to pay 100,000 silver marks, a vast sum equivalent to billions today. The details were many and each was a line-item in the contract, a copy of which remains in the Venetian state archives. Then the Venetians took a year to build the ships, and — once built — agreed on a twelve-month shipping contract to start on a certain day when the crusader army was to embark.
The Venetian Doge, chair of the city council, we might say, though an elderly man over ninety at the time, was keen on the project, and eventually sold it, with all its considerable risks, to the council and in turn to the citizenry. It meant that for a year in Venice all other activities ceased and every citizen of Venice worked on the crusader ships and all that they needed. This focus was enforced by the commune. All of this before a single silver mark had been paid.
The Arsenal became a scene of frenetic activity as ships were produced, logs were imported from Russia along with sail cloth from the England and rope from Estonia. Resources were sucked in and had to be paid for as the work went on and on.
Murphy’s Law applied. Only about a third of the projected number of crusaders arrived in Venice at the appointed day when the meter on the shipping contract started ticking.
The Venetians wanted to be paid, having outlaid nearly all of the treasury to built the crusader fleet and contract the crews, but the crusaders wanted to renegotiate the contract. When the crusaders arrived Venice was more or less broke. But the crusaders did not want to pay for thirty thousand when only twelve thousand had arrived.
Months went by and more crusaders straggled in while others gave up and left. The crusaders camped on mud flats in the lagoon where disease found them. Food was in short supply for everyone. Sanitation is best left in silence.
In the end the Venetians agreed to become participants in a joint venture rather than merely contractors for shipping, this being the only hope of securing a financial return on the massive investment the city had made in the project. They sailed.
It was not plain sailing and they diverted to Byzantium in the New Rome of Constantinople. While the Byzantines welcomed assistance against their Islamic neighbours, they were not keen on an army of thousands of ill-disciplined and increasingly desperate men camped on the foreshore, and still less interested in joining in the crusade. They had had an uneasy but durable modus vivendi with their Islamic neighbours for some time.
Many recriminations followed. Though the Pope had strictly forbade conflict among the Christians on the pain of excommunication, ultimately the Christian Fourth Crusaders attacked and sacked Christian Constantinople. The justification of this Christian on Christian war was as convoluted and tortured as that of a political candidate.
The Fourth Crusade crippled the Byzantine Empire, though it limped on for three more centuries.

Out of the pillage of Constantinople the Venetians got their 100,000 silver marks and another 150,000 for their trouble. While the other pillagers took the money and ran, the Venetians dutifully took the dosh home to Venice, along with much else from Constantinople to enrich Venice. Many of the treasures seen in Venice today, including the four lions on St Mark’s Square, were stolen from Christian Constantinople.
Venice was now the Lion of St Mark, and ruled the waves of the Eastern Mediterranean for the next three hundred years. It had bloody trade wars with rivals, mainly Genoa for a century, but it prevailed partly because of its social cohesion. It established itself on the shores of the Adriatic, Aegean, Azoz, Black, Cretan, Ionian, Levantine, and Marmara Seas.
They established and controlled sea ports, harbours, straits, estuaries, and anchorages, but they did not conquer territory or enslave populations, except on Crete. This empire was a string of settlements along shores under the flag of St Mark dotted along the Adriatic Sea into the Mediterranean Sea and eastward and north into the Black Sea. They never ventured Westward and apart from Venice itself had no settlements on the Italian coast. Nor did they risk the Red Sea to the south.
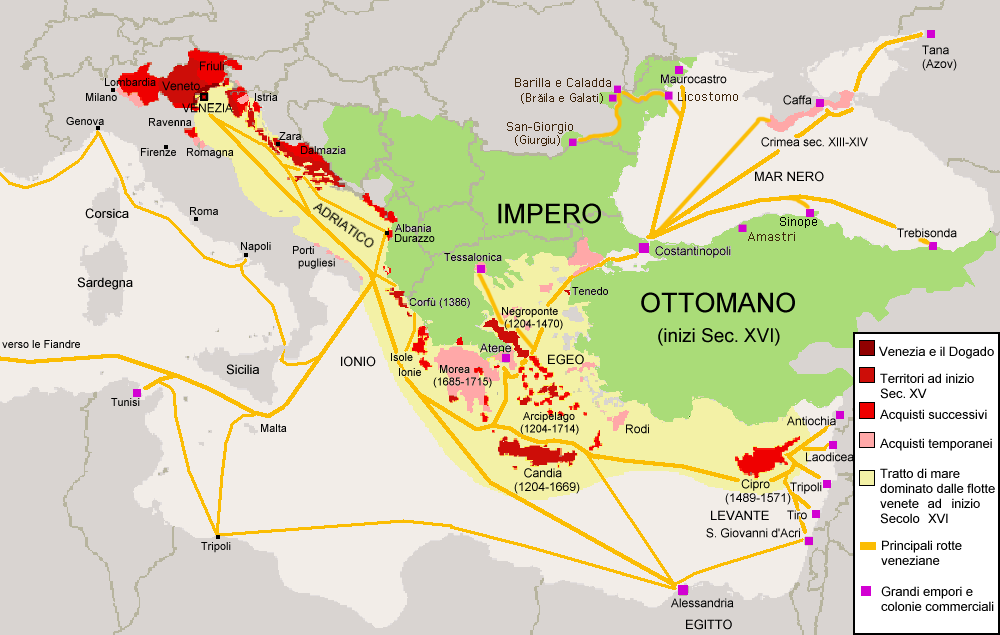 The red on the map indicates Venice’s empire of the sea.
The red on the map indicates Venice’s empire of the sea.
Venetian citizenship was closed. Venetians were forbidden to marry outside the civic list. Those Venetians who staffed, managed, and ran the empire’s outposts were strictly regulated, as two chapters of the book detail, but the real regulation was social and not legal.
Even while the Christian and Islamic worlds were at war, the Venetians happily traded with both, to the point of ferrying an Ottoman army from Asia to Europe to attack Christian peoples. In so doing the Venetians made a tremendous profit and an enduring reputation for mercenary mercantilism. Shakespeare is downwind of that.
The Silk Road brought exotic luxury goods from the Far East to the Lebanese coast and later to the Black Sea coast, and it is from these goods that Venice made astronomical profits in the high-end market.
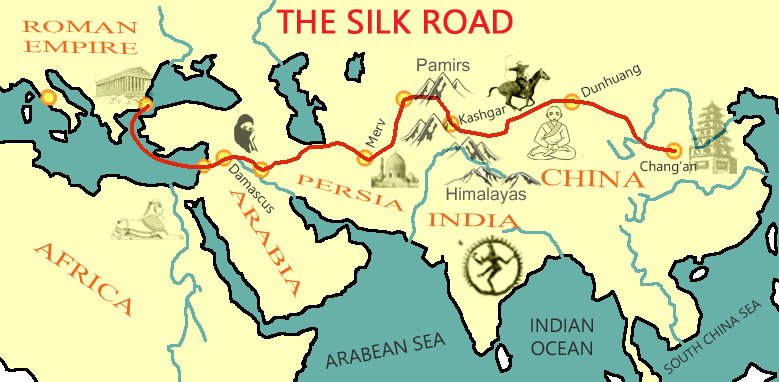
Eventually, the Ottomans began to conquer Venetian territories on the Black Sea coast, on the coasts of the Middle East, in Greece, on Crete, in Albania…. Then Venice proclaimed itself the shield of the Christian world and called for a fifth crusade to protect it. Too little, too late.
Used and abused for generations by Venice, other Christians enjoyed the spectacle of Venice supping on its just desserts. In the end Venice bought off the Ottoman but in so doing ceded most of its empire and by 1511 was just another minor city-state as the nation-states of France and Spain became European superpowers. While on a map it retained some marine territories, this was by Ottoman indulgence.
The social cohesion of Venice had disintegrated. In this telling there is no way to know which came first, the social erosion or the defeat. Which precipitated which? There is no doubt that the social discipline failed against the relentless Ottoman abrasions. Individuals enriched themselves first and secreted the money away, sometimes in other cities, like Amsterdam. Other refused to serve the commune and immigrated. While there had always been a few such deviant cases in the past, but in the Fifteenth Century they became the norm.
What finally killed Venice was not Ottoman cannons though they wounded it. Technological innovation delivered the coup de grace. When the Portuguese navigator Vasco di Gama sailed around the Cape of Good Hope to open a direct route to India, Venice’s role as an entrepôt for the Far East, e.g., spices and silk, died within a few years.
Much of the book is devoted to the many Venetian wars with Genoa and the Ottomans and the details of who killed whom in the most creative and diabolical ways. If I want blood-and-gore I can watch the television news where man’s inhumanity to man is on show every night as journalists try to shock without informing us.
The book is well written and impressively researched but did not have the insights into the social, political, ethical, religious, and financial organisation of Venice that I had sought. Many other city-states traded but somehow Venice surpassed them. How it managed, that is what makes me curious.
 Roger Crowley
Roger Crowley
Still the book lives up to its title and I can have no complaint.
A few years ago I read Garry Wills’s ‘Venice, Lion City: The Religion of Empire’ (2001). It, too, left me unsatisfied. Wills has shag carpet prose, luxurious to feel, but the book is a litany of one description of an astounding work of art, much of it devotional, after another with little or nothing about their origins and social context. This was a disappointment from an author for whom I had the highest expectations.
My prime source on Venice remains the krimis of Donna Leon and Michael Dibdin.
Skip to content
